Jupyter Lab via Hemera
To use Jupyter, select Jupyter Lab from under TReNDS interactive apps on https://hemera.rs.gsu.edu/.
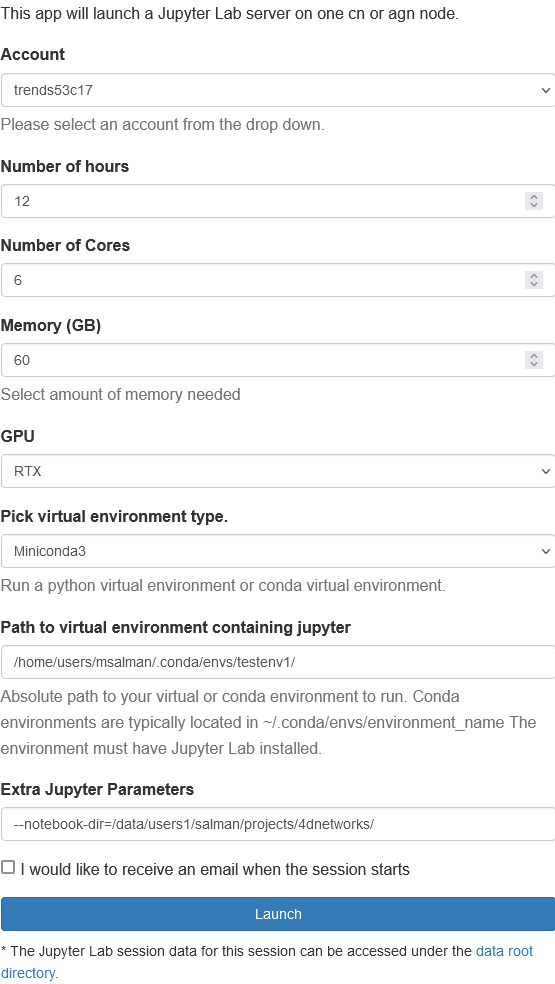
Configuring Jupyter session
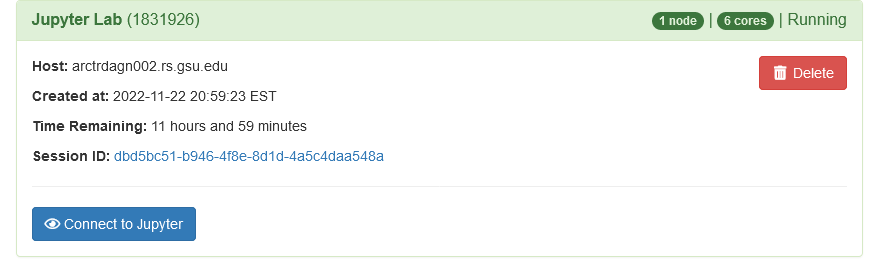
Connecting to Jupyter session

Accessing data
When configuring the session, add the working directory in the Extra Jupyter Parameters field like so:
--notebook-dir=/data/users1/salman/projects/4dnetworks/
Jupyter Lab via SLURM job
Step 1: Create SLURM bash script (jupyter_job.sh) for a jupyter job.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH -N 1
#SBATCH -n 1
#SBATCH -c 1
#SBATCH --mem=10g
#SBATCH -p qTRD
#SBATCH -t 1440
#SBATCH -J jupyter
#SBATCH --output=jupyter-%j.out
#SBATCH -A <slurm_account_code>
#SBATCH --mail-type=ALL
#SBATCH --mail-user=<email address>
#SBATCH --oversubscribe
eval "$(<path_to_conda> shell.bash hook)"
conda activate <your_enviroment>
cat /etc/hosts
jupyter-lab --ip=0.0.0.0 --port=${1:-<port>}
<path_to_conda>is fromwhich conda<your_enviroment>is your environment with installed jupyterlab:pip install jupyterlab<port>is a port that you need to select.
Step 2: Submit your Jupyter job and recover node address from file jupyter-%j.out
sbatch jupyter_job.sh
Example of jupyter-%j.out. Here you got <node> = arctrdcn010.rs.gsu.edu
# Your system has configured 'manage_etc_hosts' as True.
# As a result, if you wish for changes to this file to persist
# then you will need to either
# a.) make changes to the master file in /etc/cloud/templates/hosts.debian.tmpl
# b.) change or remove the value of 'manage_etc_hosts' in
# /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg or cloud-config from user-data
#
127.0.1.1 arctrdcn010.rs.gsu.edu arctrdcn010
127.0.0.1 localhost
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allrouters
Step 3: Run ssh tunnel to the node from the output and use port from your Jupyter.
ssh arclogin -N -f -L <port>:<node>:<port>